2025 年 8 月 1 日
Editor’s Note: Shuai, Fu, Floris Fauchet, Artak Khachatryan, Ananth Kadambi, Matt Zierhut and Anna Largajolli also contributed to this article.

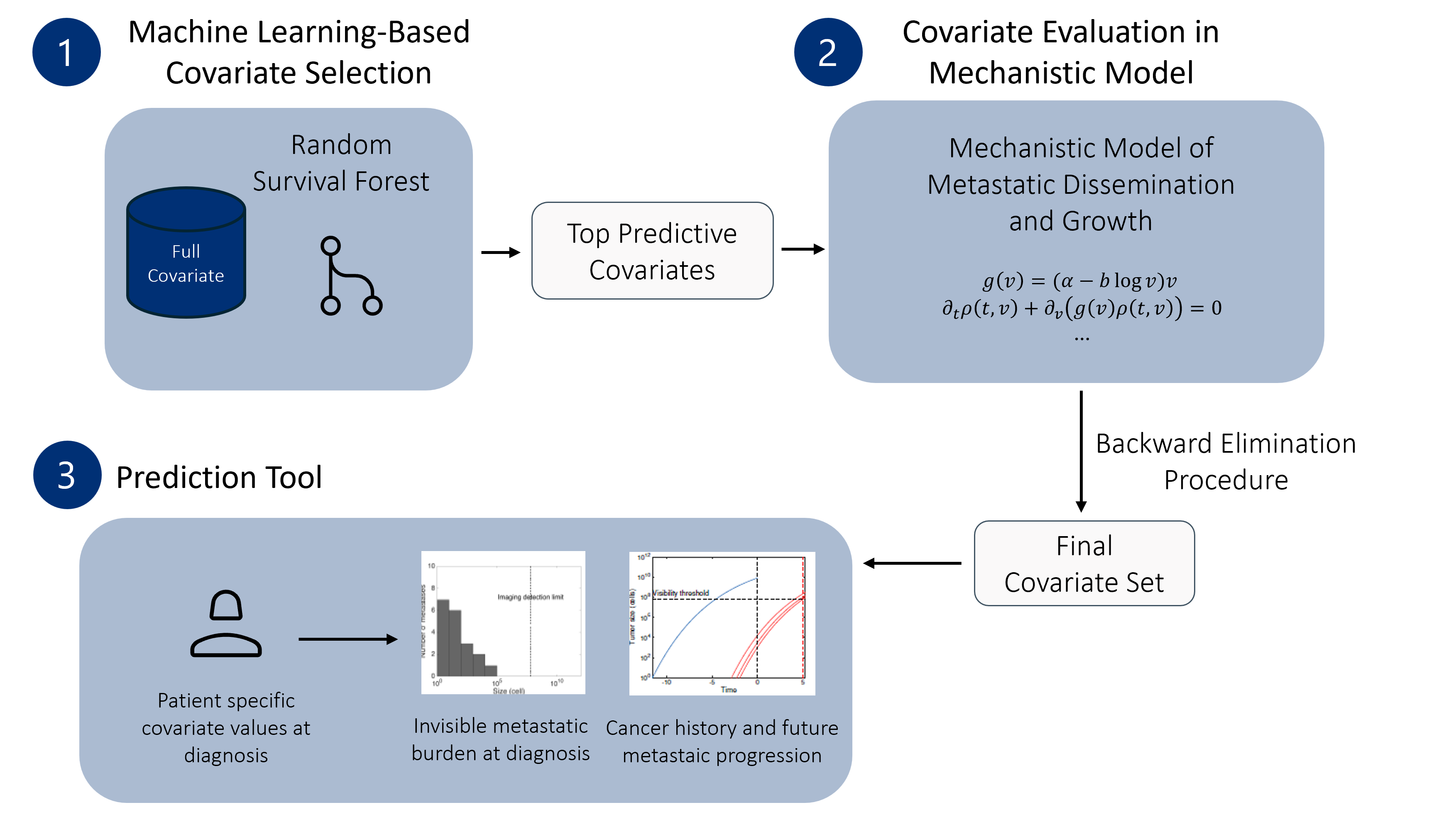
Figure 1: Workflow for covariate selection and mechanistic modeling to predict metastastic relapse in early-stage breast cancer
Certara’s experts in Real-World Evidence and Modeling can help assess whether an ML model is the right solution for your project and provide guidance on design and implementation.

Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
How can machine learning be used in healthcare?
Machine learning in healthcare can help researchers and clinicians draw faster, more reliable insights from large datasets, ultimately supporting better patient outcomes and more efficient drug development.
What role does machine learning play in healthcare data analysis?
Machine learning can be used in healthcare to analyze complex clinical and real-world patient data, enabling earlier and more accurate predictions, treatment personalization, and improved decision-making.
Why use machine learning in healthcare?
Machine learning (ML) in healthcare offers a powerful way to analyze complex, large-scale clinical and real-world patient data, enabling more accurate predictions, personalized treatments, and informed decision-making. ML models outperform traditional statistical methods in identifying key patient covariates, predicting clinical outcomes (such as metastatic relapse in early-stage breast cancer), and automating data-intensive processes like systematic literature reviews for model-based meta-analyses. These capabilities allow healthcare researchers and developers to efficiently uncover insights, reduce bias, and enhance the reliability and scalability of evidence generation — all critical for advancing patient care and drug development.
参考文献
1 Nicolò C, Périer C, Prague M, Bellera C, MacGrogan G, Saut O, et al. Machine Learning and Mechanistic Modeling for Prediction of Metastatic Relapse in Early-Stage Breast Cancer. JCO Clin Cancer Inform. 2020;4:259-74.
2 Ibtissem Rebai VD, Ayman Akil, James Craig, Mike Talley, Anna Largajolli*, Floris Fauchet*. mlcov: New Machine Learning Based R package for Covariate Selection. PAGE2024; 2024.
3 Muthukrishnan R, Rohini R, editors. LASSO: A feature selection technique in predictive modeling for machine learning. 2016 IEEE international conference on advances in computer applications (ICACA); 2016: Ieee.
4 Kursa MB, Rudnicki WR. Feature selection with the Boruta package. Journal of statistical software. 2010;36:1-13.
5 Chen W, Li L, Ji S, Song X, Lu W, Zhou T. Longitudinal model–based meta-analysis for survival probabilities in patients with castration-resistant prostate cancer. European Journal of Clinical Pharmacology. 2020;76:589-601.
6 Gonzalez RDLF, Cabra A, Liu D, Gueco M, Naslazi E, Fu S, et al. Comparative Safety of Ultrasound Enhancing Agents: A Systematic Review and Bayesian Network Meta-Analysis: Comparative Safety Evaluation of Optison. The American Journal of Cardiology. 2024.
7 Certara. CODEX [cited 2025 27 Feb]. Available from: https://codex.certara.com/codex/.
8 RAJESH M, REDDY MS, D MADHU KHR, SAI K, KUMAR KS, SINGH DBR. Interpretml: A unified framework for machine learning interpretability. 2019.
9 Arya V, Bellamy RK, Chen P-Y, Dhurandhar A, Hind M, Hoffman SC, et al., editors. Ai explainability 360 toolkit. Proceedings of the 3rd ACM India joint international conference on data science & management of data (8th ACM IKDD CODS & 26th COMAD); 2021.
Epidemiology Technical Consultant
Nina Shigesi is a technical consultant at Certara for the Real-World Evidence Solutions practice. She holds a PhD in Epidemiology from the University of Oxford. Nina has worked on a diverse range of projects analyzing real-world data, including data from electronic health records, claims and patient registries. She is an author and co-author of several scientific publications on real-world evidence studies.
Scientist, Pharmacometrics
Chiara Nicoló is a consulting scientist in pharmacometrics at Certara Drug Development Solutions. She holds a degree in Mathematics from the University of Trento and earned a PhD in Applied Mathematics from the University of Bordeaux, where she focused on modeling in oncology.
Scientist, Pharmacometrics
Ibtissem Rebai is a consulting scientist in pharmacometrics at Certara Drug Development Solutions. She has expertise in mathematics and modelling, with a master’s degree in mathematical engineering and Biostatistics from Université Paris Cité. Ibtissem also earned a master’s degree in data science from Université Paris-Saclay. At Certara, she’s worked on a range of projects analysing pharmacokinetic and patient data with statistical and machine learning models.
联系我们